What Is BMR? Basal Metabolic Rate Explained
Written by MasterClass
Last updated: Jul 19, 2021 • 3 min read
Your basal metabolic rate (BMR) determines the number of calories your body burns to maintain homeostasis.
Learn From the Best
What Is Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)?
Your basal metabolic rate, or BMR, is the estimated daily calorie allowance that your body needs to perform its basic functions. This includes homeostatic activity like breathing, organ function, and reflexes. However, BMR does not factor in strenuous physical activity like running or strength training. The number of calories needed for such tasks will exceed those represented in your BMR.
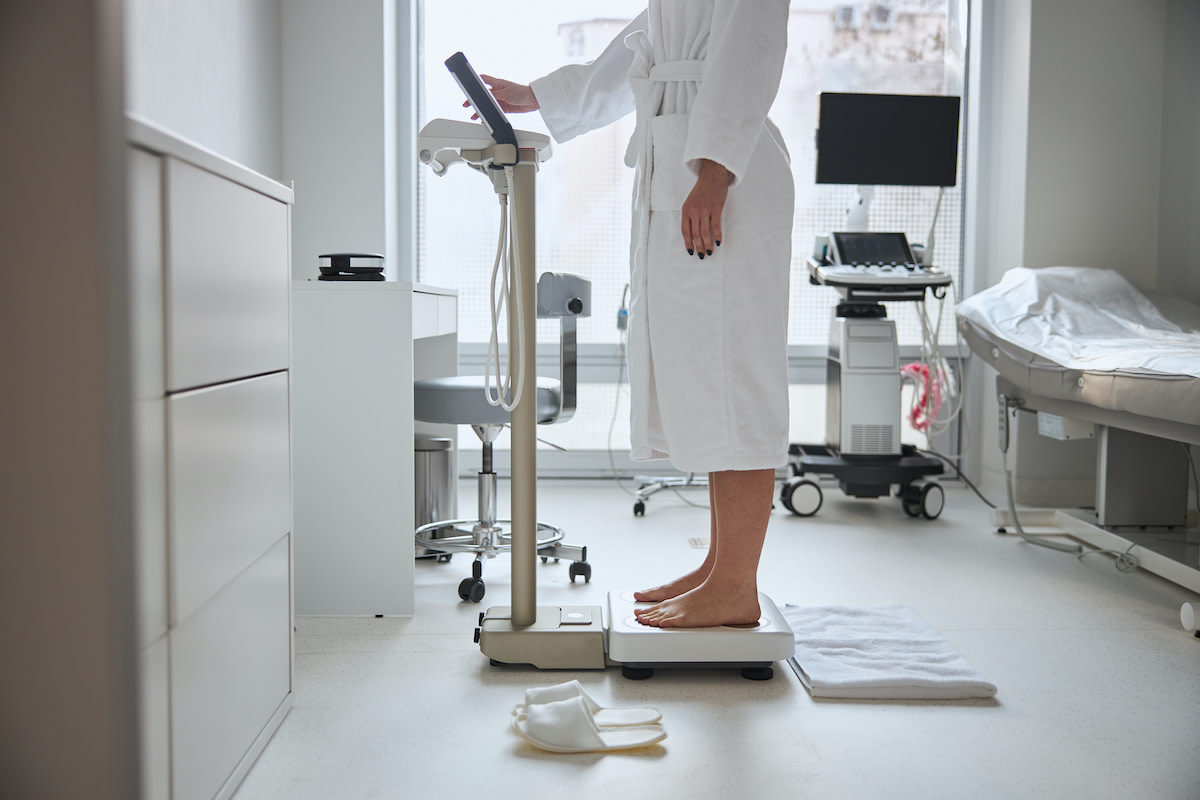
How to Calculate Your BMR
To calculate your BMR, you have three main options.
- Online calculator: Some health websites offer BMR calculators that consider multiple metrics—including the Harris-Benedict Equation and the Mifflin-St. Jeor Equation, two common BMR equations. You will be asked questions about your age, gender, current weight, height, and activity level. While not completely foolproof, these online calculators can provide a starting point for finding the caloric intake that works best for you.
- Medical devices: Some companies manufacture medical devices that measure body composition and body water levels. These devices may be too expensive for individual use, but nutritionists may purchase them to assist their clients with weight loss, weight gain, or building lean body mass.
- A doctor's visit: Perhaps the most reliable way to find your BMR is to visit a healthcare professional. Your doctor may use medical devices or the Harris-Benedict Formula to calculate your BMR. In most cases, their assessment will be more accurate than results from online tools or retail devices.
BMR vs. RMR: What’s the Difference?
BMR stands for “basal metabolic rate,” and RMR stands for "resting metabolic rate." Both calculate your resting energy expenditure, or the calorie needs associated with sitting still or lying down. They do not factor in the calories you need to perform a physical job or athletic activity.
The difference between the two comes from measuring techniques. BMR technically represents the amount of energy your body uses while lying down in a darkened room following a 12-hour fast and eight hours of sleep. An RMR reading only requires an overnight fast.
What Is Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE)?
The amount of energy you need to support your basic metabolism plus any daily activities is called Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE). BMR measures a body's caloric requirements without any physical activity, but realistically, most people engage in some form of daily activity like office work, parenting, or sports.
How to Use BMR to Calculate TDEE
You can calculate TDEE from BMR by using this formula.
- Sedentary lifestyle: If you mostly spend your days sitting at a desk or on a couch, your TDEE is 1.2 x BMR.
- Light activity: If you engage in light exercise (like walking or jogging) one to three days per week, your TDEE is 1.375 x BMR.
- Moderate activity: If you moderately exercise (running, bike riding, swimming) three to five days per week, your TDEE is 1.55 x BMR.
- Heavy activity: If you do high-level exercise (resistance training, competitive running, active team sports) six to seven days per week, your TDEE is 1.725 x BMR.
- Intense activity: If your job involves intense physical activity (heavy lifting, professional athletics) on a daily basis, your TDEE may be as high as 1.9 x BMR.
How to Use BMR When Assessing Your Diet
If you regularly eat fewer calories than you burn in your daily activities (essentially running a calorie deficit based on your BMR and your TDEE), you may lose weight. Conversely, if you take in more calories than you expend, you may gain weight. Keep in mind that if you convert body fat into lean muscle mass, you may need to increase your caloric intake because muscles require more calories while at rest.
Remember that wellness cannot be measured by a number on a scale. There is no magic weight that makes one person healthy and another person unhealthy. Work with a doctor to find the right caloric intake for you, and find physical activities you enjoy to reap the benefits of long-term health.
Want to Dive Deeper Into Your Wellness Journey?
Throw on some athleisure, fire up a MasterClass Annual Membership, and get ready to sweat it out with exclusive instructional videos from Nike Master Trainer and GQ fitness specialist Joe Holder. Want to improve your cardiovascular endurance? Give Joe’s HIIT workout a go. Trying to get a little swole? He’s got a strength training workout for that. From fitness tips to nutrition hacks, Joe will have you feeling healthier in no time.