Simmer vs. Boil: What Are The Differences?
Written by MasterClass
Last updated: Oct 11, 2021 • 2 min read
Simmering and boiling are two common cooking methods used for different purposes to achieve specific results.
Learn From the Best
What Is Simmering?
Simmering is a gentler, low-heat form of boiling liquids characterized by wisps of steam. Simmering is a slightly gentler version of boiling liquids that allows ingredients to reduce and thicken. This makes simmering a popular method for slow cooking, braising, and making reductions.
When you simmer something, there’s less movement in the pot or pan (a full boil, for example, moves things around quite a bit), so flavors can melt into one another much more seamlessly—and the structure of the individual ingredients is much better maintained. When you want to braise or stew liquids together in a pot or pan, bring the mixture to a boil to establish the heat, but then bring the temperature back down to allow the nuances to take their time and mingle.
What Is Boiling?
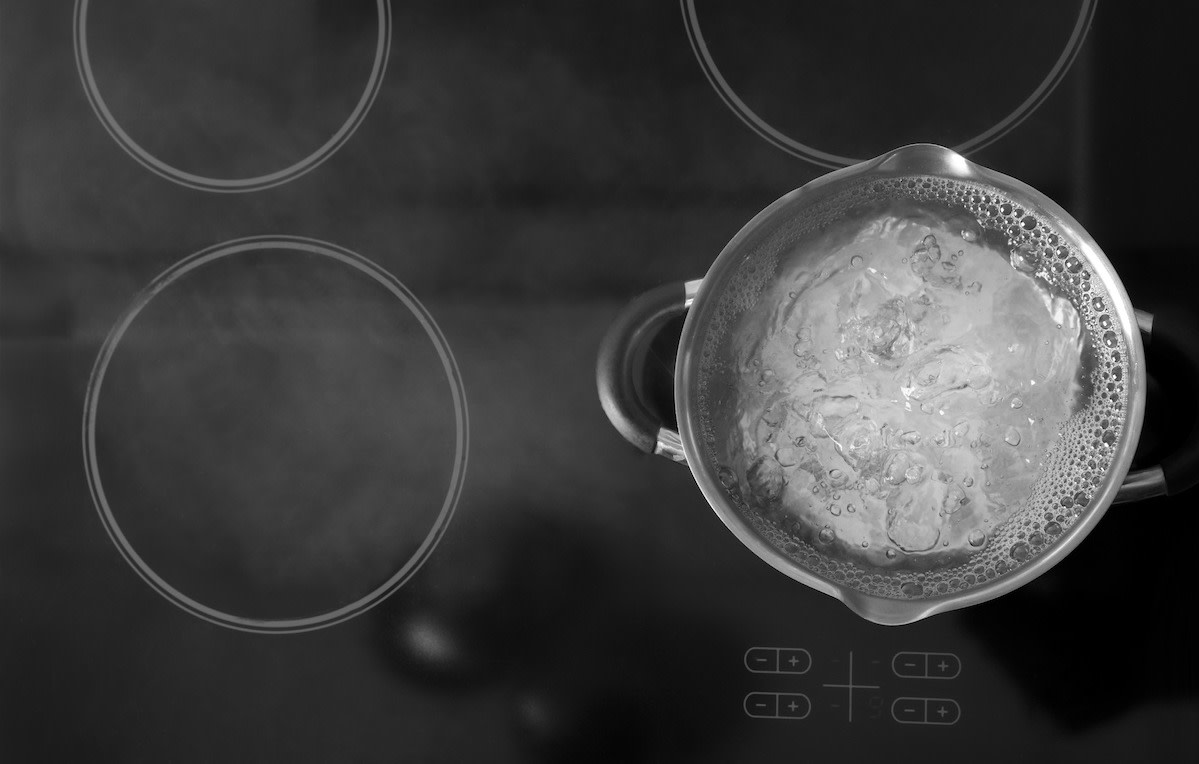
Boiling is a high-heat cooking method that involves cooking an ingredient in a rapidly bubbling and evaporating liquid. Whether you’re cooking pasta or whole grains, cooking an egg, or just need a quick blanch, boiling is a quick and clean cooking technique that involves raising the temperature of a liquid until it bubbles. The boiling temperature for a pot of water is 212 degrees Fahrenheit/100 degrees Celsius at sea level (it varies in areas with higher elevation or different atmospheric pressure).
You can boil liquids in a pot or pan on the stovetop or in the microwave. Liquids brought to a rolling boil are often used for cooking meat and pasta. You can also poach ingredients (a method of cooking food by submerging it in hot water to lock in juices) or blanch them (quickly dropping food in boiling water, then shocking it in an ice bath) in boiling liquids.
Simmer vs. Boil: What Is the Difference?
Simmering and boiling are two cooking techniques that you can use individually or in tandem. Here are some of the key differences between the two methods:
- Water temperature: Boiling involves bringing liquids to the boiling point (212 degrees Fahrenheit), which causes rapid bubbling and evaporation. Simmering requires lower temperatures (usually between 195 and 211 degrees Fahrenheit) to slowly remove moisture without evaporating too much of the liquid, which can cause it to stick to the bottom of the pot.
- Movement: The higher the temperature, the more rapidly the molecules in the liquid can move. Boiling liquids at high temperatures yields large bubbles at the bottom of the pot, which quickly rise to break the surface of the liquid. Simmering—ranging from a low simmer to a gentle boil—is characterized by a subtler movement of small bubbles from the bottom to the surface of the water.
- Uses: Simmering helps thicken sauces or make reductions. You typically use boiling for softening hard grains like pasta and rice. When you’re cooking, you should bring a liquid to a boil before reducing it to a simmering heat.
Want to Learn More About Cooking?
Become a better chef with the MasterClass Annual Membership. Gain access to exclusive video lessons taught by the world’s best, including Gordon Ramsay, Gabriela Cámara, Chef Thomas Keller, Dominique Ansel, Yotam Ottolenghi, Alice Waters, and more.